A Minimally Invasive Solution by Dr. Siddharth MBBS, MD Radiodiagnosis
Renal abscesses, though relatively rare, are serious infections that require timely and effective management to prevent complications. When antibiotics alone are insufficient, interventional procedures become necessary. One such advanced, minimally invasive technique is CT-guided catheter insertion, which offers precise drainage of the abscess. In this blog, Dr. Siddharth, an experienced radiologist, discusses the procedure, its benefits, and why it’s a vital tool in treating renal abscesses.
Understanding Renal Abscess
A renal abscess is a localized collection of pus within or around the kidney, typically resulting from a bacterial infection. Patients may present with symptoms such as fever, flank pain, chills, and malaise. If left untreated, the infection can lead to severe complications, including sepsis and permanent kidney damage.
While antibiotics remain the first line of treatment, larger abscesses often require drainage to prevent further infection and promote faster healing. This is where CT-guided catheter insertion plays a crucial role.
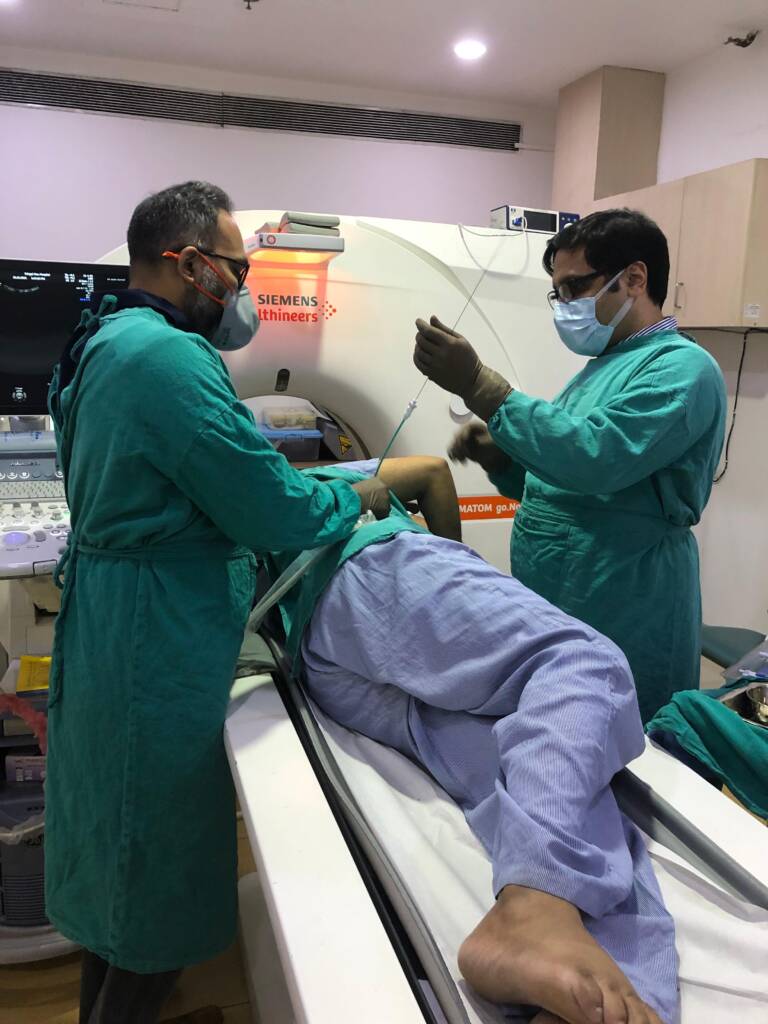
What is CT-Guided Catheter Insertion?
CT-guided catheter insertion is a minimally invasive procedure that uses real-time CT imaging to precisely guide a catheter into the renal abscess. The catheter allows continuous drainage of the abscess, facilitating faster resolution of infection and preventing recurrence.
Procedure Overview
Pre-procedure Evaluation: A thorough clinical assessment is conducted, including imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan) to evaluate the size, location, and characteristics of the renal abscess.
- Patient Positioning: The patient is positioned to allow optimal access to the abscess. The flank area is usually the point of entry, depending on the abscess’s location.
- CT Guidance: Under local anesthesia or sedation, a fine needle is inserted into the abscess under real-time CT imaging to ensure accuracy.
- Catheter Insertion: Once the needle reaches the abscess cavity, a catheter is inserted to allow continuous drainage. The catheter is typically left in place for several days until the abscess has fully drained.
- Post-procedure Care: The patient is closely monitored for infection resolution. Antibiotics are continued, and follow-up imaging is performed to assess the success of the drainage.
Why CT-Guided Catheter Insertion?
-
Minimally Invasive: Unlike open surgery, CT-guided catheter insertion is a minimally invasive procedure, reducing recovery time and hospital stays.
-
Precision: CT imaging provides real-time, high-resolution guidance, ensuring that the catheter is accurately placed, minimizing complications.
-
Reduced Risk of Complications: By avoiding open surgery, the procedure minimizes the risks associated with surgical intervention, such as blood loss, prolonged recovery, and infection.
-
Faster Recovery: Patients experience less post-procedure discomfort and can return to normal activities sooner compared to traditional surgery.
Who Benefits from This Procedure?
CT-guided catheter insertion is particularly beneficial for patients with large renal abscesses or those who are not responding to antibiotic therapy. It is also ideal for individuals who are poor candidates for surgery due to other underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
CT-guided catheter insertion for renal abscesses represents a significant advancement in interventional radiology, offering a safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment option. With precision imaging and expert care, patients can expect faster recovery and improved outcomes.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of a renal abscess or have been diagnosed with one, consult with a specialist to determine if this procedure is right for you. At D G Diagnostics, we are equipped with the latest technology and skilled professionals like Dr. Siddharth to provide cutting-edge care for renal and other medical conditions.
Contact us today for expert advice and treatment!
By Dr. Siddharth, MBBS, MD Radiodiagnosis
